Understand the electricity bill
Since 2006, all electricity consumers in mainland Portugal can choose their electricity supplier. With the liberalization of this sector, it is intended to increase competitiveness and the number of offers, so that it has an impact on reducing consumers’ bills.
The energy bill is a considerable expense in the overhead of a home. According to the household expenses survey of the National Statistics Institute, this expenditure represents 6.3% of the average annual expenditure of a family.
The free market providers define the price of energy and power taking into account that the cost of sale to the end customer must cover the costs of the purchase price of energy, the margin of the supplier and the tariff for access to the networks. In this way, offers with varying conditions and prices can be made available.
COMPONENTS IN AN ELECTRICITY INVOICE
The final price of an electricity bill consists of the following terms:
Variable Terma (Termo Variável)
Enery Price
(€/kWh)
Fixed Term (Termo Fixo)
Power Price
(€/day)
Services and Refunds (Serviços e Reembolsos)
Maintenance, etc.
(€/month)
Variable term – Corresponds to the amount paid, effectively, to the energy consumed.
Fixed term – Corresponds to the daily fixed price depending on the contracted power. For a domestic consumer, the power ranges from 1.15 to 41.1 kVA.
These terms include the values related to the network access tariff. This tariff corresponds to the amount payable for the use of network infrastructures depending on the variations in the tariffs for the use of transmission and distribution networks and the tariff for the global use of the energy policy and economic and general interest (CIEG) cost system. Additionally, the value of the tariff of the Logistics Operator for the Change of Supplier (OLMC) is included.
The network access tariff is defined annually by ERSE with a fixed price and applied both in the free and regulated markets.
Fees and Taxes – There are currently 3 fees and taxes applied to the electricity bill, the Exploration Fee of the General Directorate of Energy and Geology (DGEG), the Special Consumption Tax (IEC) and the Audiovisual Contribution (CAV).
Electricity bill terms
Energy Consumption
In case there is an actual reading in the period to be billed, the measured consumption is shown and in the case of no readings on site, the estimated consumption. The amount payable on this component is calculated by multiplying the contracted unit price and consumption.
Example: For a monthly consumption of 150 kWh and a contracted unit price of € 0.1608 / kWh, there is an amount to pay for the energy consumed of € 24.12.

Contracted Power
For a residential consumer in Low Normal Voltage the power varies between the step 1.15 to 41.1 kVA defined by the simultaneous use of equipment. The price varies depending on the offer or trader and is defined in the contract. To calculate this installment, the number of days in the period to be invoiced is multiplied by the price of the contracted power price.
Example: For a monthly invoice and fixed term of € 0.2220 / day, the customer pays € 6.66.
Fees and taxes are mandatory and applied by traders through the invoices issued:
Exploration Fee Direção Geral de Energia e Geologia – DGEG
It represents a fixed fee (0.07 €) defined by DGEG, whose value reverts to the State, for the use and exploitation of electrical installations.
Special Consumption Tax – IEC
It falls under the category of tax on petroleum and energy products (ISP). The fixed fee is € 0.001 per kWh of energy billed.
Example: For a monthly consumption of 150 kWh, € 0.15 tax is paid.
Note: Consumers entitled to a discount on the social electricity tariff are exempt from paying this installment.
Audiovisual Contribution – CAV
It is intended to finance the public service of radio broadcasting and television (Law no. 30/2003, of 22 August). In this case, the value is delivered by the traders to the Tax Authority that delivers to Rádio e Televisão de Portugal SGPS, S.A.
The value is fixed monthly of 2.85 €, so it must be paid 12 times a year by each consumer.
Note: Some customers may be exempt from paying this fee or reduced payment of it. This applies, for example, to annual consumption of less than 400 kWh or with special financial conditions. Consumers entitled to a discount on the social electricity tariff pay a reduced amount of € 1 / month.
Additional services and refunds are optional offers applied by retailers to differentiate their products:
Additional Services
The additional services are part of the offers of several suppliers and allow to obtain more favorable energy prices. When subscribing to them, there is usually an associated loyalty of 12 months, thus allowing traders to present more competitive values. These services may include the maintenance of household appliances, construction work, insurance, among others.
Example: For an additional service of € 150 / year, the customer pays € 12.50 per month for this service.
Refunds
Some merchants have loyalty programs that allow refunds of a percentage of the invoice amount. This amount can be deducted directly from the amount payable or made available on discount cards.
Example: A 6% discount on the total amount of an invoice of € 40 / month, is equivalent to a refund of € 2.40.
What are you paying for?
Breakdown of the prices of the components of an invoice
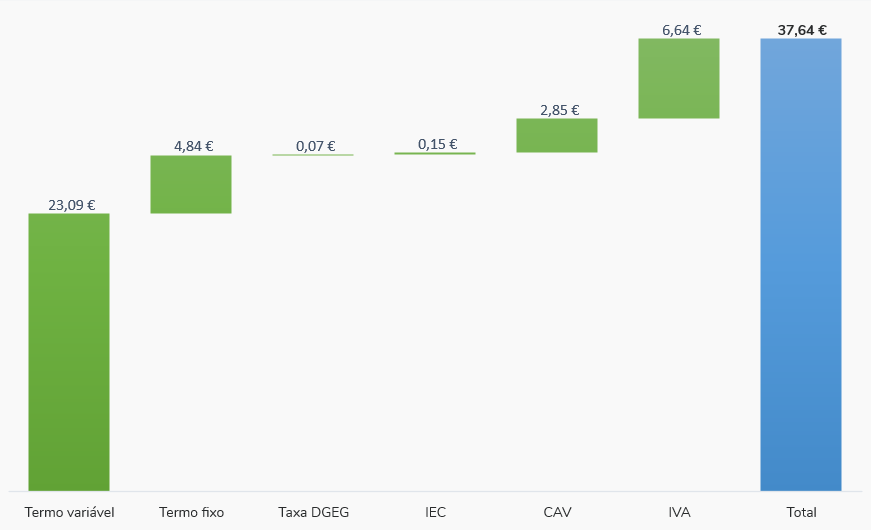
Considering a family of two adults and a child, an average monthly electricity consumption of 150 kWh is obtained.
For this case, a contracted power of 4.60 kVA was also considered, with a simple tariff and the family opted for the electronic invoice and the payment by direct debit.
Thus, there is a breakdown of the amounts payable for each installment, calculated with the prices of the most advantageous tariff at the moment, without additional services or refunds, which has a unit price of the variable term of 0.1539 € / kWh and a fixed term unit price of € 0.1614 / day.
Recommendations
- In addition to energy, you can choose a tariff with additional services, which allows you to contract services that go beyond energy, for example, equipment maintenance, insurance, among others. These services are detailed in the energy bill and you must validate that they are correctly billed.
- If you still do not have an operational smart meter, you must send the readings to your distributor or dealer monthly. Thus, it avoids estimates.
- Check out our tips and learn how to reduce your energy bill;
- Currently, you can choose and compare among the more than 250 offers that vary on several factors such as payment method, invoice submission and additional services.
- Register on our website and you will regularly receive news and alerts to perform a new simulation;
- Make a simulation regularly, in order to check the most advantageous offers on the market.



 Simulador Simples
Simulador Simples Simulador Avançado
Simulador Avançado